In the vast expanse of the cosmos,where humans have ventured to unravel its mysteries,an unforeseen consequence has emerged from our advancements: space junk. These countless man-made objects, ranging from discarded spacecraft to tiny debris, orbit our planet, posing an escalating threat to Earth’s infrastructure and human presence in space. As we delve into the realm of space junk, an expert elucidates its nature, the risks it poses, and the pressing need for thorough solutions. Join us on this illuminating journey as we unravel the story of space junk and its potential impact on our future.
Space Junk: An Increasing Threat to Earth
The Growing Menace of Space Junk:
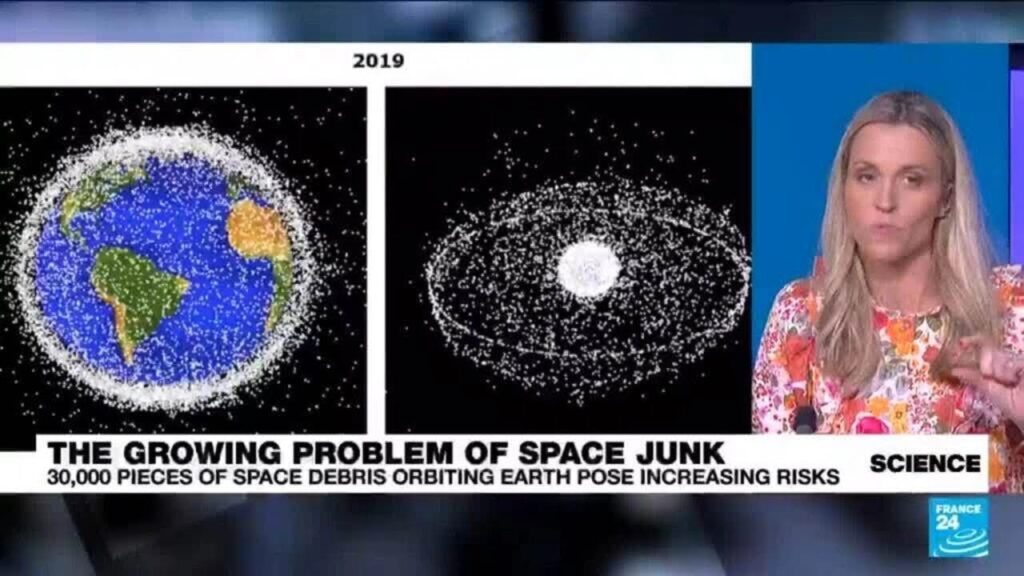
Space junk, or orbital debris, consists of defunct satellites, rocket fragments, and other man-made objects orbiting our planet at alarming velocities. This ever-expanding field of debris poses a meaningful threat to Earth’s satellites, space exploration missions, and even human life. With each new launch, the density of space junk increases, raising the likelihood of catastrophic collisions. These high-impact events shred satellites into countless smaller pieces, perpetuating a dangerous cycle of debris generation. The escalating presence of space junk highlights the urgent need for responsible waste management, collision prevention measures, and innovative approaches to mitigate this growing threat to our planet and its exploration.
The Nature of Space Debris and its Sources
The Nature of Space Debris and Its Sources
Space debris, also known as space junk, is a term used to describe human-made objects no longer in use that remain in space, orbiting Earth. It includes everything from inactive satellites, discarded rocket stages, to small fragments of debris. The sources of space debris are numerous, including:
Abandoned satellites – satellites that have reached the end of their operational lives and have been left in orbit. These satellites may no longer function,but thay continue to pose a potential risk to other satellites and spacecraft.
Spent rocket stages and launch vehicle components - These are discarded during rocket launches and can remain in space for years or decades.
Collision fragments - When satellites or spacecraft collide, pieces of debris from the impact may be scattered into orbit.
Intentional destruction - In certain specific cases, satellites or spacecraft have been deliberately destroyed, creating large amounts of debris.
* Micrometeoroids – Meteoroids that are too small to be visible by the naked eye but can damage satellites and spacecraft.The amount of space debris has been increasing steadily over the years, prompting concerns about its potential impact. Space debris poses a risk to satellites and spacecraft, as well as to astronauts and ground-based infrastructure. As space activity continues to expand, the problem of space debris is likely to become more severe unless measures are taken to mitigate its effects.
Risks Posed by Space Junk: Collision Hazards and Re-entry Threats
Collision Hazards and Re-entry Threats:
Space junk can pose significant threats to satellites and spacecraft. Its high-speed orbit makes even small pieces of debris hazardous.Collisions with space junk can damage or disable satellites, affecting communications, navigation, and weather forecasting. The International Space Station (ISS), which orbits at an altitude of about 400 kilometers, has had to maneuver to avoid collisions with space debris multiple times.
Table: Example of Space Junk Removal Mission
| mission | Target | Outcome |
|—|—|—|
| e.Deorbit | Envisat satellite | Accomplished, spacecraft deorbited and re-entered Earth’s atmosphere |
| Astroscale | Debris removal | Developed technologies to capture and remove space debris |
Mitigation Strategies: Removing and Reducing Debris
One way to mitigate the risk posed by space junk is to remove and reduce it. This can be done through active debris removal (ADR) missions, which involve using spacecraft to physically remove debris from orbit, or through passive debris removal (PDR) techniques, which aim to reduce the amount of debris generated in the first place. ADR missions are still in their early stages, but there are a number of promising concepts that could be developed in the future. PDR techniques, conversely, are already being implemented, and include measures such as designing spacecraft to be more resistant to debris impacts and requiring satellites to deorbit at the end of their lifespan.
To Wrap It Up
as our celestial canvas becomes increasingly cluttered with manmade debris, we stand at a crossroads of space exploration and environmental stewardship. The issue of space junk serves as a testament to the double-edged nature of technology and challenges us to find innovative solutions that balance our terrestrial advancements with the preservation of our extraterrestrial neighborhood. It’s time we navigate this cosmic minefield responsibly,ensuring that future generations can continue to gaze up at the starlit sky with wonder and awe,unmarred by the remnants of our technological footprints.